The Ortho Molecular Products Magnesium Family
For more than 35 years, we’ve remained committed to delivering high-quality, research-backed, therapeutically effective products sold exclusively to health care professionals. As the nutraceutical industry continues to grow, we value your trust, and your patients’ trust, in our products and the consistent outcomes they provide.
All our magnesium products offer highly bioavailable forms of magnesium for minimal gastrointestinal side effects and maximum results.
Choosing the Right Magnesium for Your Patients
Our magnesium products are formulated to deliver absorbable forms of magnesium, but one product may be more appropriate depending on individual needs. Use this easy-to-reference chart to help you choose the best option for your patients.
| Product Name | Product Bottle | Attributes | Dosage | Servings per Bottle | Resources* | |
Magnesium Family | Reacted Magnesium |  |
| 235 mg per 2 capsules | 30, 60 & 90 | |
| Reacted Magnesium Powder |  |
| 300 mg per scoop | 30 | ||
| Mag Threonate |  |
| 144 mg per 2 capsules | 30 |
*Contact your Account Executive or email us to order product newsletters, patient educational brochures and catalogs.
The Magnesium Deficiency Epidemic
Magnesium is the fourth-most abundant mineral in the body and is required for what is estimated to be over 600 enzymatic and intracellular processes. Unfortunately, studies have found that up to 60% 1 of American do not consume the Recommended Dietary Allowance of magnesium. The RDA is 320 mg and 420 mg of magnesium for women and men, respectively.
Over half of the population cannot meet their nutritional magnesium needs for several reasons. First, produce is estimated to contain 80-90% less magnesium than it did a century ago. Additionally, ultra-processed foods are now the primary calorie source of the American population, and food processing depletes 80-90% of the magnesium content of food. Magnesium can be depleted further in the body due to diet, medications, aging, exercise and stress.

Source: Workinger J, Doyle Robert, Bortz J. Challenges in the Diagnosis of Magnesium Status. Nutrients. 2018;10(9):1202. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10091202
Dietary choices can influence magnesium status by either impairing absorption or promoting renal excretion of magnesium. When magnesium is consumed at the same time as soft drinks containing phosphoric acid or fluoridated water, magnesium becomes bound and precipitates, leading to impaired absorption. Magnesium and calcium have natural antagonism in the human body, which begins with competition for absorption in the intestines. A diet high in sodium, protein or diuretic beverages like caffeine or alcohol-containing drinks can cause enhanced renal wasting of magnesium. 2,3
Impairment of absorption or renal wasting are the mechanisms of action for magnesium-depleting pharmaceutical drugs like diuretics, proton pump inhibitors, insulin and bisphosphonates. Aging is an established association with magnesium deficiency. Exercise is important for mental-emotional and whole-body health, however, both short-term and long-term exercise deplete magnesium. 2,4,5
Magnesium Absorption Mechanisms
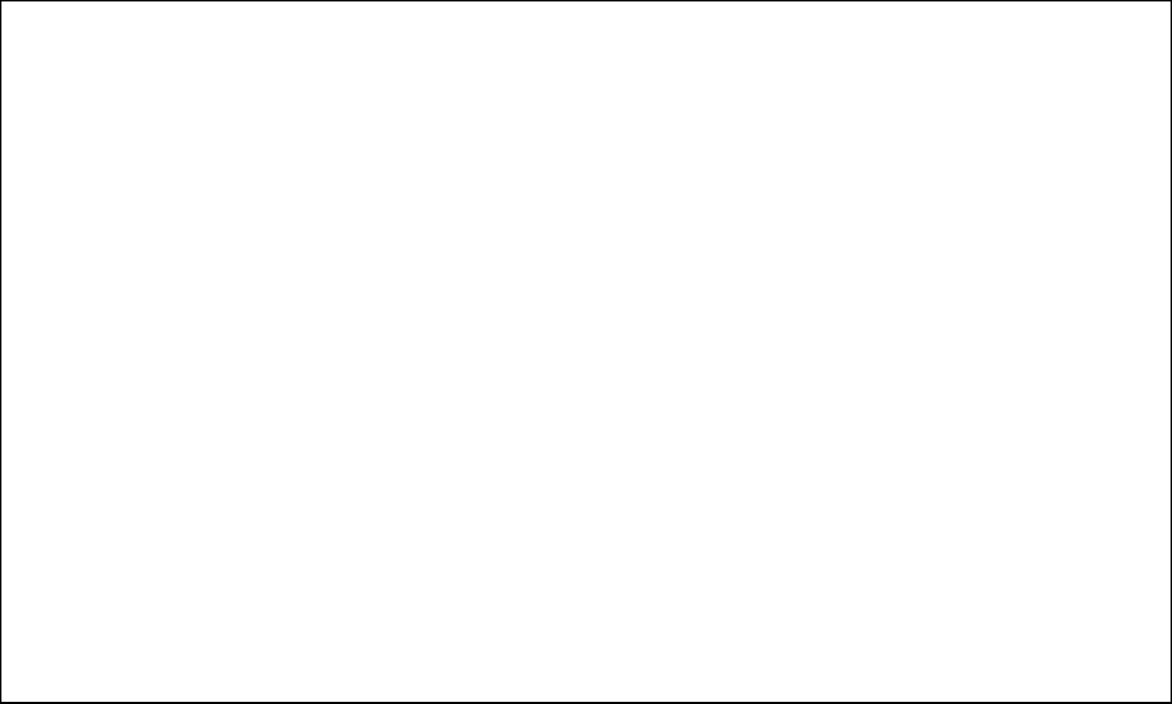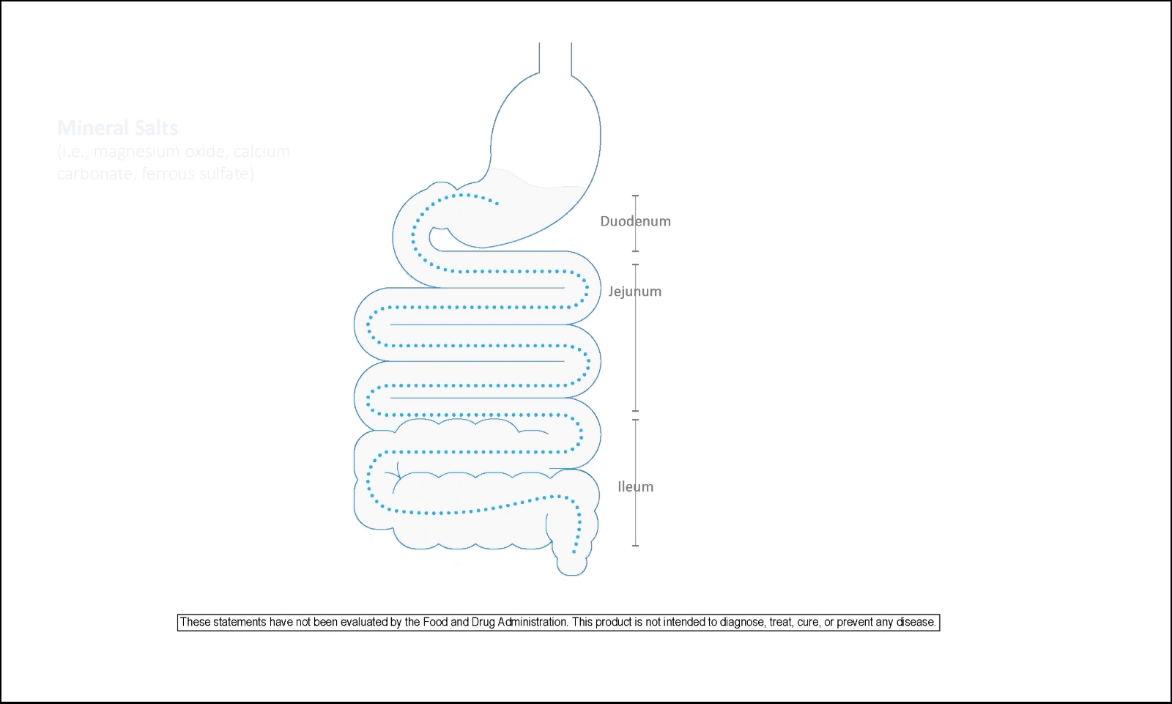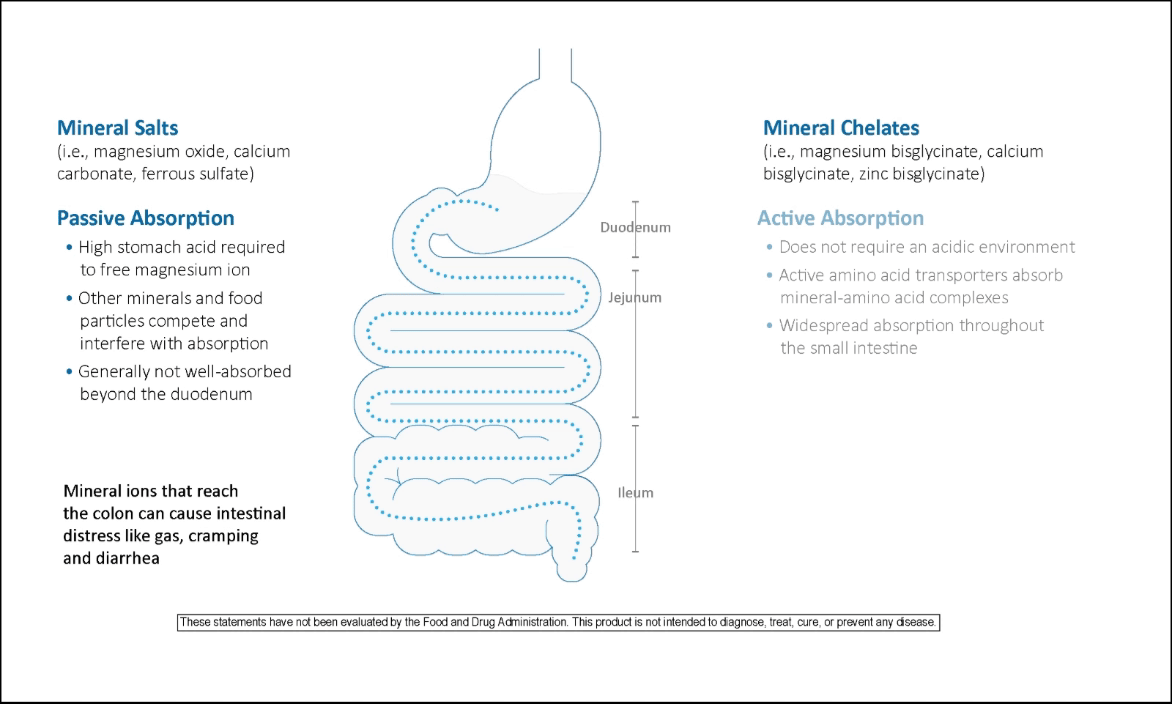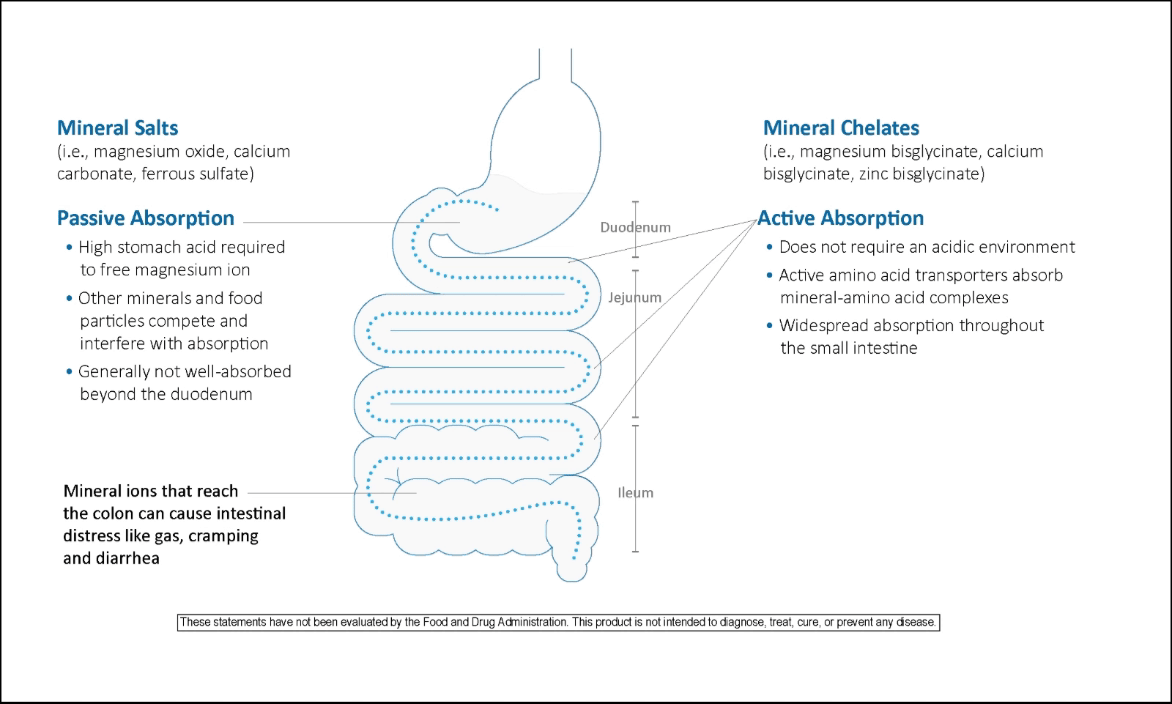
The human body has three primary mechanisms to absorb magnesium. Absorption of magnesium depends on the form of magnesium and the location within the intestine. In the correct environment, magnesium salt can dissociate from its salt complex to be absorbed passively by paracellular absorption. Magnesium transporters on the epithelial cell surface can also actively absorb magnesium salt ions from the intestinal lumen. The third mechanism by which magnesium is absorbed is through chelation of the magnesium to amino acids. Magnesium chelated to amino acids is absorbed actively through amino acid transporters.
Absorption Comparison of Mineral Salts vs. Mineral Chelates in the Intestine
Threonic Acid and Brain Magnesium
Magnesium is vital for the health of the whole body, but it has particularly important actions within the brain. A sufficient level of magnesium is critical for the health and function of the brain, as some of its most important functions are to protect the integrity of the blood-brain barrier, attenuate the inflammatory cascade, support the synthesis of neurotransmitters and nitric oxide, modulate GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) and NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) receptors. The transportation of magnesium from serum to cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and then into the neurons of the brain is a complex, multi-step process because of the tight regulation of magnesium in serum.
Threonic acid, or threonate, is a naturally occurring sugar acid that has been investigated for its ability to enhance delivery of magnesium into the CSF and neuronal cells in as little as two weeks. Threonic acid can associate with the GLUT 1 receptors on the choroidal epithelial cells of the blood-brain barrier to facilitate the transportation of magnesium into the CSF. In the CSF, threonic acid can then associate with the GLUT 3 receptors to enhance magnesium transportation into neuronal cells. Transportation into the CSF and neuronal cells occurs in a concentration-dependent manner. Compared to other forms of magnesium compounds, magnesium L-threonate is the only form of magnesium scientifically demonstrated to increase magnesium concentration within the brain. 6

1. de Baaij JHF, Hoenderop JGJ, Bindels RJM. Magnesium in man: implications for health and disease. Physiological reviews. 2015;95(1):1-46. doi:https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00012.2014
2. Pickering G, Mazur A, Trousselard M, et al. Magnesium status and stress: The vicious circle concept revisited. Nutrients. 2020;12(12):3672. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12123672
3. Workinger J, Doyle Robert, Bortz J. Challenges in the Diagnosis of Magnesium Status. Nutrients. 2018;10(9):1202. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10091202
4. Gröber U. Magnesium and Drugs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019;20(9):2094. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092094
5. Volpe SL. Magnesium in Disease Prevention and Overall Health. Advances in Nutrition. 2013;4(3):378S383S. doi:https://doi.org/10.3945/an.112.003483
6. Sun Q, Weinger JG, Mao F, Liu G. Regulation of structural and functional synapse density by L-threonate through modulation of intraneuronal magnesium concentration. Neuropharmacology. 2016;108:426-439. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.05.
*Cannot be combined with any other offer, promotion, or discount. Applies to Ortho Molecular Prodcuts branded products only. Must purchase 12 of the same SKU to receive 2 FREE. Offer expires 12/31/24




